Evaluators and Automating Model Tuning, Model Metrics
Overview
As mentioned in the previous article on Decisioin trees, it is possible to tune model parameters automatically. For example, regression and classification have the same core model tuning functionality. The automation approach would be to select evaluator, pick metric to optimize for and then train pipeline to do the parameter tuning.
Each so selected model can be evaluated against standard metrics as offered by RegressionMetrics Spark Scala and Python objects:
Setting up the parameter tuning pipeline
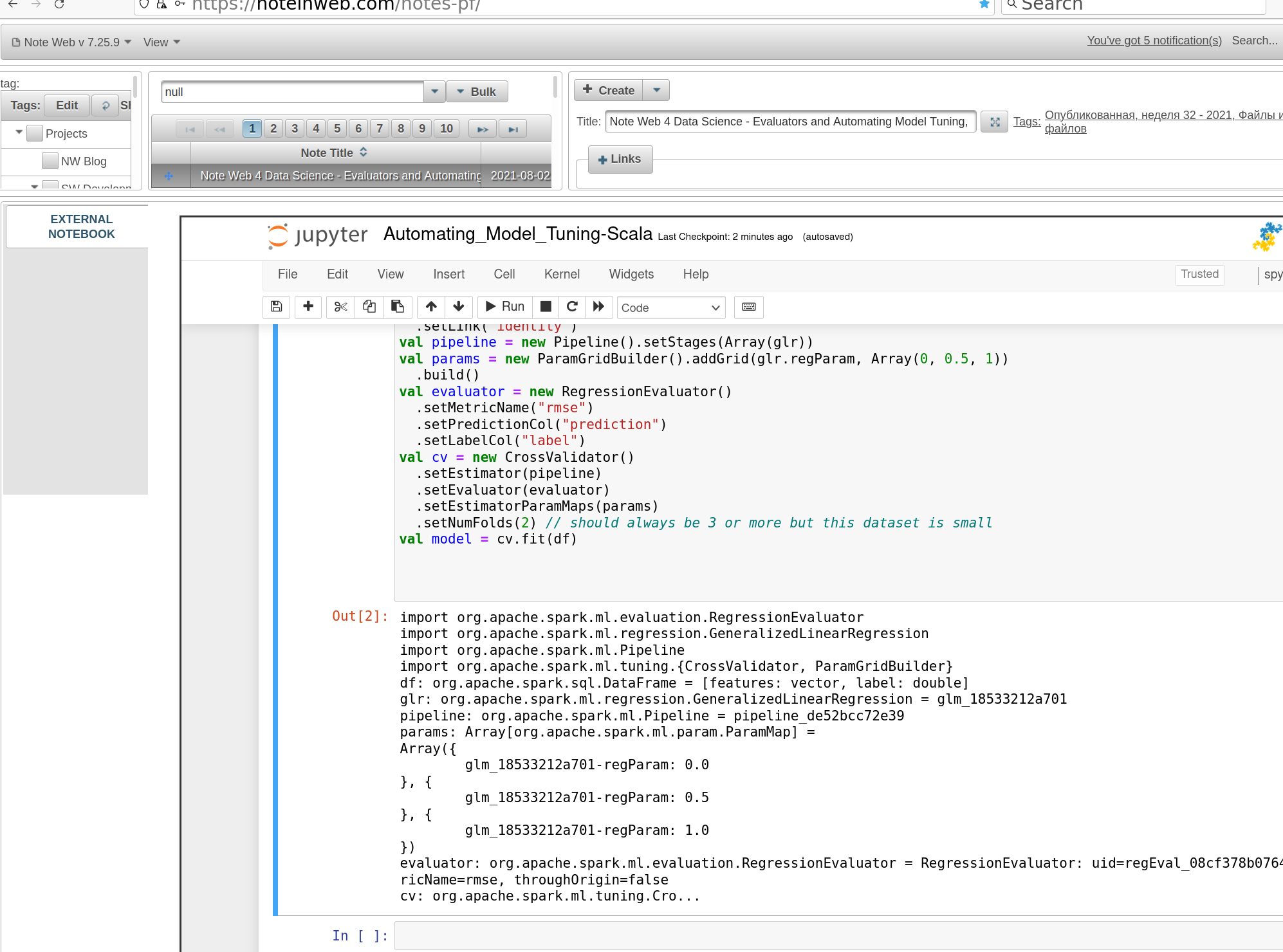
RegressionEvaluator is used to build the pipeline, as in sample below:
- RMSE is metric to optimize against
importorg.apache.spark.ml.evaluation.RegressionEvaluatorimportorg.apache.spark.ml.regression.GeneralizedLinearRegressionimportorg.apache.spark.ml.Pipelineimportorg.apache.spark.ml.tuning.{CrossValidator,ParamGridBuilder}valglr=newGeneralizedLinearRegression().setFamily("gaussian").setLink("identity")valpipeline=newPipeline().setStages(Array(glr))valparams=newParamGridBuilder().addGrid(glr.regParam,Array(0,0.5,1)).build()valevaluator=newRegressionEvaluator().setMetricName("rmse").setPredictionCol("prediction").setLabelCol("label")valcv=newCrossValidator().setEstimator(pipeline).setEvaluator(evaluator).setEstimatorParamMaps(params).setNumFolds(2)// should always be 3 or more but this dataset is smallvalmodel=cv.fit(df)
Assessing other top model's metrics
importorg.apache.spark.mllib.evaluation.RegressionMetricsvalout=model.transform(df).select("prediction","label").rdd.map(x=>(x(0).asInstanceOf[Double],x(1).asInstanceOf[Double]))valmetrics=newRegressionMetrics(out)println(s"MSE =${metrics.meanSquaredError}")println(s"RMSE =${metrics.rootMeanSquaredError}")println(s"R-squared =${metrics.r2}")println(s"MAE =${metrics.meanAbsoluteError}")println(s"Explained variance =${metrics.explainedVariance}")

References
- ISBN 978-1491912058 Jake VanderPlas "Python Data Science Handbook: Essential Tools for Working with Data 1st Edition "
Note In Web, Inc. © September 2022-2026; Denys Havrylov Ⓒ 2018-August 2022